Hydraulics of Sediment Oxygen Demand Chambers
Investigators:
- Prof. Joseph Hun-wei Lee
- Dr. C. P. Kuang
- Dr. K.S. Yung
¡@
Introduction
The Sediment Oxygen Demand (SOD) is the rate of oxygen consumption exerted by the bottom sediment on the overlying water. In relatively shallow nutrient-rich coastal waters in Hong Kong, where algal blooms frequently occur, the SOD can be substantial, and may lead to severe oxygen depletion, resulting in massive fish kills. Sediment oxygen consumption rates can be measured in situ by a SOD chamber mounted over the seabed. A flow of water is artificially generated above the sediment to simulate the natural environment and to create full mixing within the chamber; the SOD is determined from the drop in dissolved oxygen concentration upon passage over the sediment. Previous field and laboratory studies have demonstrated that the SOD is strongly dependent on the water velocity above the sediment. The objective of this project is to study the hydrodynamics of the flow in SOD chambers, and the oxygen transfer across the sediment-water interface.
¡@
|
|
|
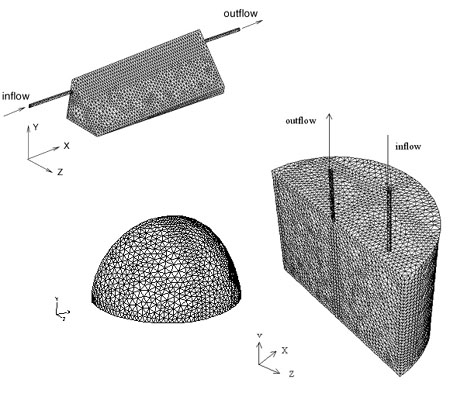
Computational mesh in numerical solution of
SOD chamber flow |
¡@
¡@
The three-dimensional flow field inside SOD chambers of rectangular, cylindrical, triangular and dome-shaped geometries have been successfully computed. Supported by experiments, the flow predictions help explain the discrepancy of previous filed measurements using different chambers, and improved our understanding of the sediment-water interface, a water quality model has also been developed to predict the sediment oxygen demand in coastal waters.
¡@
|
|
|
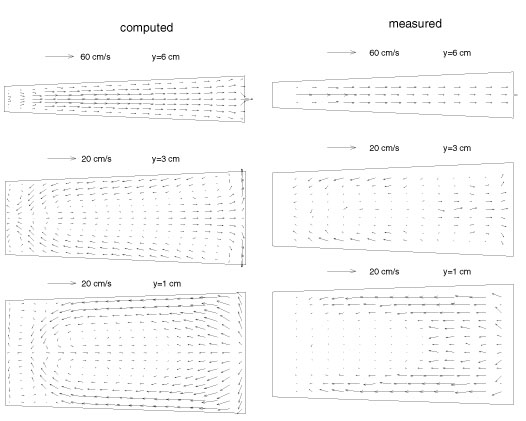
Computed and measured horizontal
flow field above the sediment in a triangular SOD chamber,
L=30cm, w=15cm, H=8cm for a through flow rate of Q=120L/h |
¡@
The flow field above the sediment depends strongly on the chamber geometry. In a triangular chamber, significant reverse flows and secondary circulations can be generated; the over bottom velocity can be 10 times the average displacement velocity, the SOD measurement is hence strongly related to the chamber design
¡@
|
|
|
|
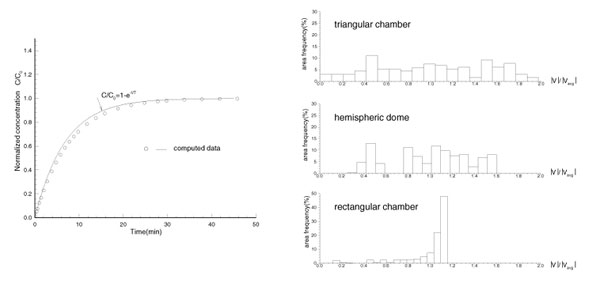
Computed variation of tracer
concentration due to step input of tracer mass |
Predicted flow distribution above
a sediment for three generic SOD chamber designs |
¡@
¡@