Field Investigation to the East River Basin
¡@
¡@
Field Investigation to the East River Basin
Nine field investigations to the East River Basin have been conducted from 2004 to 2006 during both dry and wet seasons, to obtain first hand information of land use, geomorphology and river flow characteristics. Samples of water quality, algal and macro-invertebrate macro bio-diversity have also been collected.
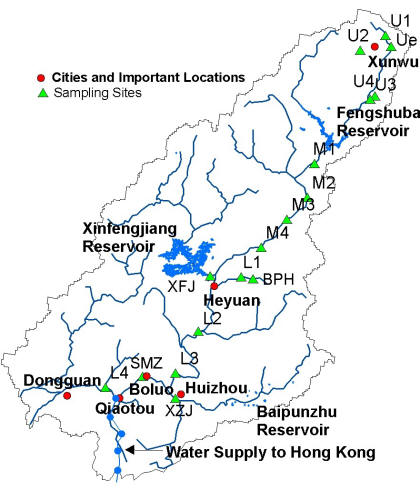
¡@
|
Algal bio-diversity sampling ¡@ |
Drifting sampling of macro invertebratebio-diversity ¡@ |
 Macro invertebrate bio-diversity sampling ¡@ |
 On site water quality measurement ¡@ |
|
Laboratory Analysis (suspended solid) |
Laboratory Analysis (Colorimetry) |
¡@
River Health Indices
Several indices are set up to quantitatively correlate the biodiversity with water quality.
¡@
1. Water Quality Index (WQI): Water Quality Index (WQI, Štambuk-Giljanović, 2003) ranges from 0 to 100, and is based on the measured values of temperature, DO, pH, conductivity, NH4 + NO3, PO4 and TSS. For each parameter, a score is given and the scores are aggregated by a weighting factor to obtain the river health index
![]() ,
,
where Q=score, and W=weighting factor
¡@
2. Shannon-Wiener Index (H): H is a measurement of community algal diversity calculated by using the number of species (N) and the number of individuals in each species (n)
![]()
¡@
3. Taxon Richness: A direct measurement of the number of species in a sampling site
Water Quality
Common water quality parameters (DO, pH, conductivity, temperature) are measured on site, and samples are taken for subsequent analysis for nutrients and suspended solids using standard methods.
¡@
In general, the water quality in the East River is better than other large rivers in China. In the dry season, the water quality in the upper and middle reaches (e.g. above Heyuan) is well exceeds the Chinese National Water Quality Grade II standard. Towards the river mouth, below Boluo, however, there is notable organic pollution. The same spatial trend is observed in the wet season; the higher NH4 concentrations measured may be contributed by non-point pollution sources brought to the river by rainfall and overland flow.
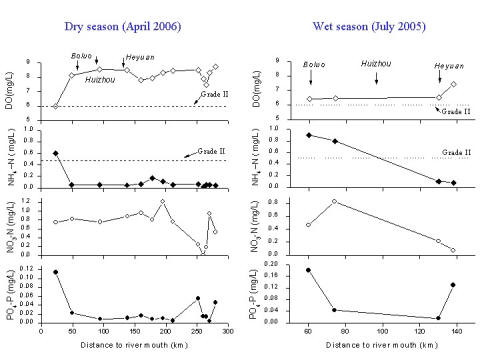
¡@
¡@
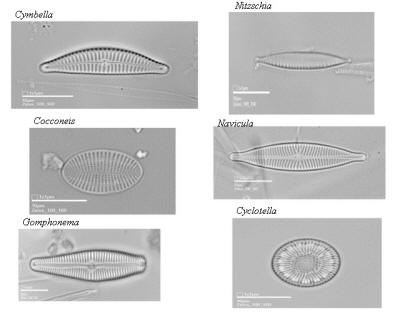
Algal bio-diversity
Algal bio-diversity analysis has been performed in 4 sites (BPH and XFJ in the Heyuan city, XZJ and SMZ in the Huizhou city) in the East River Basin. WQI is generally around 80 near Heyuan but decreases to around 50 in the downstream reaches near Huizhou. WQI and the algal bio-diversity do not appear to be correlated. H falls within the typical range of 1.5-3.5; at the XFJ site below the Xinfengjiang Reservoir, the low bio-diversity is believed to be related to the reservoir operation.
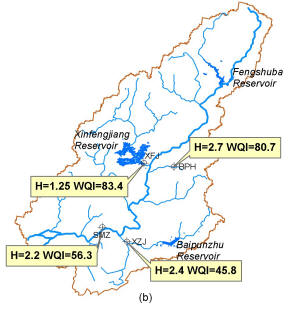
¡@
¡@
Benthic macro-invertebrate
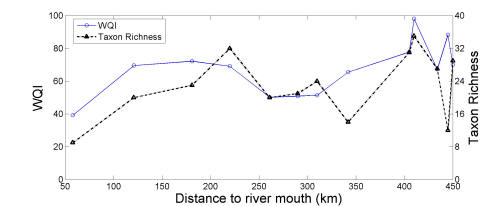
Thirteen sites have been surveyed from upstream tributaries to the lower reaches of the East River to collect benthic invertebrates and environmental data. A total of forty-one insect families have been found. A positive relationship is found between WQI and taxon richness, with a correlation coefficient of 0.63. The highest and the lowest relative abundance happened in the cleanest site (U3) and the dirtiest site (L4) respectively, reflecting a high correlation between water quality and benthic macro-invertebrate.
¡@
|
Odonata |
Diptera |
Ephemeroptera |
Trichoptera |
¡@
¡@
Concluding Remarks
The field data show that the water quality is generally good in the upper and middle reaches, and well exceeds drinking water quality standards. Due to anthropogenic activities, the water quality deteriorates in the downstream reaches towards the river mouth. Benthic macro-invertebrate diversity is correlated with water quality.
¡@







